1. Preface
My interest in Evolutionary Algorithms started when I read On the Origin of Circuits over at DamnInteresting.com. I always wanted to try something like that out for myself, but never really found the time. Now I have, and I think I’ve found some interesting results.
Disclaimer: I know next to nothing about Evolutionary Algorithms. Everything you read in here is the product of my own imagination and tests. I may use the wrong algorithms, nomenclature, methodology and might just be getting very bad results. They are, however, interesting to me, and I do know something about evolution, so here it is anyway. After writing this article I have gone over it once more and have added the correct names (crossover, elitism, etc) to the corresponding sections.
2. How Evolution Works
So, how does an Evolutionary Algorithm work? Why, the same as normal biological evolution, mostly! Very (very) simply said, organism consist of DNA, which determine their characteristics. When organisms reproduce, there is a chance their offspring’s DNA contains a mutation, which can lead to difference in characteristics. Sufficiently negative changes in offspring make that offspring less fit to survive, causing it, and the mutation, to die out eventually. Positive changes are passed on to future offspring. So through evolution a set of DNA naturally tends to grow towards its "goal", which is ultimate fitness for its environment. Now this is not an entirely correct description, but for our purposes it is good enough.
3. A simple evolutionary algorithm
There is nothing stopping us from using the same technique to evolve things towards goals set by a programmer. As can be seen from the Antenna example in the DamnInteresting article, this can sometimes even produce better things than engineers can come up with. In this post, I’m going to evolve the string "Hello, World!" from random garbage. The first example won’t be very interesting, but it demonstrates the concept rather well.
First, lets define our starting point and end goal:
source = "jiKnp4bqpmAbp" target = "Hello, World!"
Our evolutionary algorithm will start with "jiKnp4bqpmAbp", which we can view as the DNA of our "organism". It will then randomly mutate some of the DNA, and judge the new mutated string’s fitness. But how do we determine fitness? This is probably the most difficult part of any evolutionary algorithm.
3.1. Fitness function
Lucky for us, there’s an easy way to do this with strings. All we have to do is take the value of each character in the mutated string, and see how much it differs from the same character in the target string. This is called the distance between two characters. We then add all those differences, which leads us to a single value which is the fitness of that string. A fitness of 0 is perfect, and means that both strings are exactly the same. A fitness of 1 means one of the characters is off by one. For instance, the strings "Hfllo" and "Hdllo" both have a fitness of one. The higher the fitness number, the less fit it actually is!
Here’s the fitness function.
def fitness(source, target):
fitval = 0
for i in range(0, len(source)):
fitval += (ord(target[i]) - ord(source[i])) ** 2
return(fitval)
If you look closely, you’ll notice that for each character, I square the difference. This is to convert any negative numbers to positive ones, and to put extra emphasis on larger differences. If we don’t do this, the string "Hannp" would have a fitness of 0. You see, the difference between 'e' and 'a' is -5, between 'l' and 'n' is +2 (which we have twice) and between 'o' and 'p' is +1. Adding these up yields a fitness of 0, but it’s not the string we want at all. If we square the differences, they become 25, 4, 4 and 1, which yields a fitness of 34. Effectively, we square each difference so that they can’t cancel each other out.
In the mutation algorithm below, I only mutate one character by one value at a time. It has been pointed out that, unless I actually allow for larger mutations, squaring the distance is largely pointless, since new mutations will always only differ by one value. At the time I wrote this fitness function, I had no idea how the rest of the algorithm would look like. It seemed like a good idea.
3.2. Mutation function
Now we need to introduce mutations into our string. This is rather easy. We simply pick a random character in the string, and either increment or decrease it by one, or leave it alone:
def mutate(source):
charpos = random.randint(0, len(source) - 1)
parts = list(source)
parts[charpos] = chr(ord(parts[charpos]) + random.randint(-1,1))
return(''.join(parts))
Time to tie the whole shabang together!
fitval = fitness(source, target)
i = 0
while True:
i += 1
m = mutate(source)
fitval_m = fitness(m, target)
if fitval_m < fitval:
fitval = fitval_m
source = m
print "%5i %5i %14s" % (i, fitval_m, m)
if fitval == 0:
break
This should be easy enough to understand. For each iteration of the While-loop, we mutate the string and then calculate its fitness. If it is fitter then the original string (the parent), we make the child the new string. Otherwise, we throw it away. If the fitness is 0, we’re done!
3.3. Results
Lets look at some output. I’m snipping out some intermediary output cause it’s not terribly interesting.
At generation 1, we have a fitness of 15491, and the string looks nothing like "Hello, World!". The same for generation 20, 40, 60, etc.
1 15491 jjKnp4bqpmAbp 20 15400 jiKnp3bppoAbp 40 15377 jiKlo2bpooAdp 60 15130 iiKlo2aoooAdp
Not much progress so far. At generation 500 it’s still a load of nonsense:
500 9986 \eTlo,YaorNdf
Generation 1200, we start to see something that looks like "Hello, World!":
1200 4186 Heglo,LWorhdP
Generation 1500, we’re getting very close!
1500 3370 Hello,GWorldL
It still takes a good 1500 generations more before we’re finally there:
3078 2 Hello, Vorld" 3079 2 Hfllo, World" 3080 2 Hfllo, World" 3081 0 Hello, World!
There it is!
4. A better, more interesting, algorithm
Okay, so that worked. But… it was kinda lame. Nothing interesting to see, really, was there? That’s because our algorithm was a little too simplistic. Only one "organism" in the gene pool, only one character mutated at any time. We can do better than that, so let’s modify the program to make it more interesting.
4.1. Gene pool
We’re not going to touch our fitness function, since that works rather well. Instead, lets introduce a gene pool. Instead of having only one string, why not have a whole bunch or randomly generated strings and let them duke it out among themselves. That sounds a bit more real-life, doesn’t it?
GENSIZE = 20
gene pool = []
for i in range(0, GENSIZE):
dna = [random.choice(string.printable[:-5]) for j in range(0, len(target))]
fitness = calc_fitness(dna, target)
candidate = {'dna': dna, 'fitness': fitness }
gene pool.append(candidate)
This little snippet generates a gene pool with 20 random strings and their fitnesses. In an official implementation, the gene pool would be called the population.
4.2. Crossover
Now, lets modify our mutation function. Instead of mutating one single character, we feed it two parents, picked at random from the gene pool, and it will mix their DNA together a bit. This is called crossover. It will also randomly mutate one character in the resulting DNA. It then returns the newly fabricated child, including its fitness.
def mutate(parent1, parent2):
child_dna = parent1['dna'][:]
# Mix both DNAs
start = random.randint(0, len(parent2['dna']) - 1)
stop = random.randint(0, len(parent2['dna']) - 1)
if start > stop:
stop, start = start, stop
child_dna[start:stop] = parent2['dna'][start:stop]
# Mutate one position
charpos = random.randint(0, len(child_dna) - 1)
child_dna[charpos] = chr(ord(child_dna[charpos]) + random.randint(-1,1))
child_fitness = calc_fitness(child_dna, target)
return({'dna': child_dna, 'fitness': child_fitness})
We perform crossover by taking a random part of the second parent’s DNA and copying it over the first parent’s DNA. We also perform a random mutation of one character, just like in our simple example.
4.3. Elitism
We also need a routine to pick two random parents from the gene pool. Now, we could just pick them completely random, but what you really want is for parents with a good fitness to have a better chance of offspring. This is called elitism. If we sort the gene pool list by fitness, we can use a uniform product distribution to make sure that parents with better fitness get chosen more often.
Now you might ask, what the hell is a uniform product distribution? When you randomly pick a number between, say, one and ten, each number has the same chance of being picked. This is called a "uniform distribution". But when you pick two random numbers, and you multiply them, there’s a much bigger chance of getting a bigger number than a smaller number. Hence the name "uniform product distribution". Here’s how that looks:
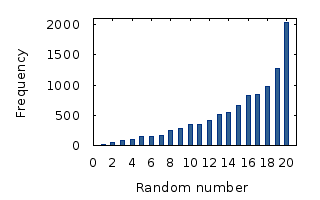
So our random parent picker will do just that. We select two random real numbers between 0 and 1, multiple those two random numbers and then scale the result up to our poolsize by multiplying the result with the size of the pool. We return that parent from the pool.
def random_parent(gene pool): wRndNr = random.random() * random.random() * (GENSIZE - 1) wRndNr = int(wRndNr) return(gene pool[wRndNr])
There! Now it’s time for our main loop
while True:
gene pool.sort(key=lambda candidate: candidate['fitness'])
if gene pool[0]['fitness'] == 0:
# Target reached
break
parent1 = random_parent(gene pool)
parent2 = random_parent(gene pool)
child = mutate(parent1, parent2)
if child['fitness'] < gene pool[-1]['fitness']:
gene pool[-1] = child
For each iteration of the While True loop, we first sort the gene pool by fitness so that the most fit parents are at the top. We check to see if the fittest happens to be the target string we’re looking for. If so, we stop the loop.
Then we select two parents from the gene pool using the uniform product distribution so that fitter parents are chosen more often. We create a bastard mutated child that will mix both parents' DNA together and introduce a little mutation. If the new child is more fit than the worst in the gene pool, it will replace that degenerate one in the gene pool. In the next iteration, the pool is sorted again on fitness so that the new child takes its rightful place.
4.4. Results
Now it’s time to run this puppy and see what it does. Again, I snip out some of the less interesting stuff.
Here’s the gene pool in the beginning. The first number is the generation (the number of times the While-loop has run), the second number the fitness and the third column is the DNA for that entry in the gene pool. Interesting entries are marked with callouts in the form of <1>, <2>, etc.
1 7617 'iSx{$,K`u~(B
1 9284 SQf`1N#UdrPlT <1>
1 12837 sYIu<E"Fq'^_.
1 15531 DC8Dg1I$*mUs-
1 16064 L~*}JBVdF7bu2
1 16533 1,XU%)5$q[YuO
1 16588 ff],ceW<0fud& <2>
1 17316 [V3@2'VgY\{KV
1 17356 kWw#v/P<#apG9
1 17581 <Lrh(1hN_Bd)3
1 18777 TM]_]TbtxFY:q
1 19656 $zS+EI?BS>%z(
1 19841 =S;B~((W8 D,6
1 20398 P_A$D|NPJPio/
1 21957 J&f=O:g\8'{S2
1 22543 5*T2c"pMZ80L'
1 24954 A&lZ#A_}MxI"P
1 25186 &9MrI|0&x)q,N
1 28110 OlXT/Q{y3{"LR
1 29656 8WB99hx%0]}h[
One big random jumbled mess. Note the ones I’ve emphasized, <1> and <2>. These are the parents that were selected for the new child in the next generation. Lets see how it looks after one generation:
2 7617 'iSx{$,K`u~(B
2 8742 SQf`1N#UdfumT <1>
2 9284 SQf`1N#UdrPlT
2 12837 sYIu<E"Fq'^_.
2 15531 DC8Dg1I$*mUs-
2 16064 L~*}JBVdF7bu2
2 16533 1,XU%)5$q[YuO
2 16588 ff],ceW<0fud&
2 17316 [V3@2'VgY\{KV
2 17356 kWw#v/P>#apG9
2 17581 <Lrh(1hN_Bd)3
2 18777 TM]_]TbtxFY:q
2 19656 $zS+EI?BS>%z(
2 19841 =S;B~((W8 D,6
2 20398 P_A$D|NPJPio/
2 21957 J&f=O:g\8'{S2
2 22543 5*T2c"pMZ80L'
2 24954 A&lZ#A_}MxI"P
2 25186 &9MrI|0&x)q,N
2 28110 OlXT/Q{y3{"LR
Two random parents from the previous generation have their DNA mixed, and have generated an offspring (<1>) which is better then both of them. It comes in second with a fitness of 8742, while its parents only had fitness of 9284 and 16588. Lets skip ahead a bit and look at the 6th generation:
6 7617 'iSx{$,K`u~(B
6 8742 SQf`1N#UdfumT <1>
6 9284 SQf`1N#UdrPlT <2>
6 10198 SQfD1N#UdfumT <3>
6 12837 sYIu<E"Fq'^_.
6 15531 DC8Dg1I$*mUs-
6 16064 L~*}JBVdF7bu2
6 16387 SQf`1N"MZ80LT <4>
6 16533 1,XU%)5$q[YuO
6 16588 ff],ceW<0fud&
6 17316 [V3@2'VgY\{KV
6 17356 kWw#v/P>#apG9 <5>
6 17356 kWw#v/P>#apG9 <6>
6 17581 <Lrh(1hN_Bd)3
6 18777 TM]_]TbtxFY:q
6 19656 $zS+EI?BS>%z(
6 19841 =S;B~((W8 D,6
6 20287 fe],1eW<0fud&
6 20398 P_A$D|NPJPio/
6 21957 J&f=O:g\8'{S2
As you can see, the "SQf" has reproduced again with success, and there are now four variants (<1> to <4>) of it in the gene pool. We also note the "kWw#", which there are two identical ones of (<4> and <5>). This can happen when the entire DNA of one parent is copied and no mutation occurs. In our mutate function, we use the first parent’s DNA as a base and then randomly overlay some of the seconds parent’s DNA. This can be anything from the entire second parent’s DNA, or nothing at all. But generally, the chance is higher that the first parent’s DNA survives largely in tact.
The next interesting generation is 13:
13 4204 RQf`{$,KdfumT
13 7617 'iSx{$,K`u~(B
13 7617 'iSx{$,K`u~(B
13 8742 SQf`1N#UdfumT
13 8742 SQf`1N#UdfumT
13 9284 SQf`1N#UdrPlT
13 9284 SQf`1N#UdrPlT
13 10198 SQfD1N#UdfumT
13 12837 sYIu<E"Fq'^_.
13 15531 DC8Dg1I$*mUs-
13 15838 L~*xJBVdG7bu2
13 15856 $zS+<E"Fq(^_(
13 15883 L~*xJCVdG7bu2
13 16064 L~*}JBVdF7bu2
13 16387 SQf`1N"MZ80LT
13 16533 1,XU%)5$q[YuO
13 16588 ff],ceW<0fud&
13 17316 [V3@2'VgY\{KV
13 17356 kWw#v/P>#apG9 <1>
13 17356 kWw#v/P>#apG9 <2>
Wow! "SQf" has been really busy and now almost rules the gene pool. "iSx" is second and third, but has lost its number one position to the "RQf" variant of "SQf". "RQf" was introduced in the 12th generation as a child of an "iSx" and "SQf" variant. We see that "kWv" has been knocked almost to the end of the list by more fit candidates. It is very obvious that this pool is no longer random. Patterns are starting to emerge all over it.
By the time we reach generation 40:
40 3306 RQSw{$-KcfumB
40 4204 RQf`{$,KdfumT <1>
40 4229 RQf`|$,KdfumT <2>
40 4242 RQe`|$,KdfumT
40 4795 RQSw{$-KdfumT
40 4971 RQSwz$*K`uSnT <3>
40 4973 RQSwz$+K`uSmT <4>
40 4992 RQSwz$+K`uSnT <5>
40 5017 SQSxz$+K`uSmT
40 5017 SQSxz$+K`uSmT
40 5951 (QSxz$+KdfSmT
40 5985 'QSxz$+K`uSmT
40 6421 SQfx{$+K`u~(B
40 6444 TQf`{$+K`u~(B
40 6489 SQfx{$+KdfS(B
40 6492 TQf`{$-K`u~(B
40 7034 SQSxy$+KdfS(B
40 7617 'iSx{$,K`u~(B
40 7617 'iSx{$,K`u~(B
40 7625 'iS`{$,Kdg~(B
The gene pool is now almost entirely dominated by the "RQf" variants. Forms of its original parents "SQf" and "iSx" can still be found here and there, although "iSx" is almost entire gone from the pool. An interesting thing is that we can see combinations of letters (<1> to <5>) that keep reappearing: "$,KdfumT" and "RQSwz". These are almost like actual genes! Combinations of DNA that work well together and therefor stay in the gene pool in that combination. It takes lots of generations to make variants of these genes that are more fit then previous versions.
The next milestone is found in the 67th generation:
67 3138 RQSw{$+KdfukA
67 3161 RQSw{$+KcfukA
67 3176 RQSw{$,KdfulA
67 3176 RQSw{$+KcfulA
67 3218 RQSw{$-LcfumA
67 3222 RQSw{%,KefumB
67 3237 RQSw{$-LcfvmA
67 3241 RQSw{$-KcfumA
67 3241 RQSw{$-KcfumA
67 3266 RQSw{$-KceumA
67 3266 RQSw{$-KceumA
67 3267 RRSw{$-KcfumB
67 3289 RQSw{%,KefumC
67 3306 RQSw{$-KcfumB
67 3306 RQSw{$-KcfumB
67 3323 RQSw{#-KcfumB
67 3324 RPSw{$-KdfumB
67 3331 RQSw{$-KbfumB
67 3348 RQSw{#-KbfumB
67 3489 RQSw{$+KdfumA
This marks the first generation where there are no other variations then the RQS one. But immediately, we see the next generation in which a new number one is found:
68 3119 QQSw{$+KdfukA
68 3138 RQSw{$+KdfukA
68 3161 RQSw{$+KcfukA
By the 96th generation, QQS has taken over the top:
96 3060 QQSw{%+KdhukA
96 3065 QRSw{%+KdfukA
96 3081 QQSw{%+KdgukA
96 3081 QQSw{%+KdgukA
96 3081 QQSw{%+KdgukA
96 3096 QQSw{$+KdgukA
96 3104 QQSw{%+KdfukA
96 3119 QQSw{$+KdfukA
96 3119 QQSw{$+KdfukA
96 3119 QQSw{$+KdfukA
96 3137 RRSw{$,KdfulA
96 3137 RRSw{$,KdfulA
96 3138 RQSw{$+KdfukA
96 3138 RQSw{$+KdfukA
96 3138 RQSw{$+KdfukA
96 3138 RQSw{$+KdfukA
96 3138 RQSw{$+KdfukA
96 3142 QQSw{$,KdfukA
96 3142 QQSw{$+KcfukA
96 3144 QQSw|$+KdfukA
This is where the race gets boring. Every now and then a new, better, mutation will arise and take over the gene pool. Change is slow though, and no big surprised are left. The candidates slowly but surely mutate until the reach something resembling the "Hello, World!" we are looking for in generation 1600:
1600 19 Hdllo+ Worle% 1600 20 Hdklo+ Worle% 1600 20 Hdklo+ Worle% 1600 20 Hdklo+ Worle% 1600 20 Hdklo+ Worle% 1600 20 Hdklo+ Workd%
It takes almost another half-thousand generation to get to the final target:
1904 0 Hello, World! 1904 1 Hello, World" 1904 1 Hello, World" 1904 2 Hello, Wprld" 1904 2 Helmo, World" 1904 2 Helmo, World" 1904 2 Hdllo, World" 1904 2 Hello, Worle"
5. Conclusions
Interesting (if you’re boring like me and you like this kind of stuff) facts:
-
It usually takes anywhere between 2500 and 4000 generations to evolve the target.
-
On average, it takes approximately 3100 generations to evolve the target.
-
If we remove the parent DNA mixing and rely solely on mutations, it takes on average 3650 generations to evolve the target.
-
The parent DNA mixing is only really useful in the beginning. In the first generations, it can quickly propel a new mix of DNA to the top of the list, but later on random mutations instead of mixing DNA becomes the main driving force between the evolution. (this doesn’t have to be the case in real life evolution, naturally)
-
Sometimes "beneficial" mutations disappear. For instance, the word "World" already appeared in mutation 1469, but was overtaken by other mutations quickly. It was pushed out of the gene pool at generation 1486, only to reappear in generation 1659. From then on, it quickly rose to the top and dominated the top 5 positions of the gene pool within 10 generations.
It has rightly been pointed out that there are much more efficient methods of this algorithm. Please keep in mind that I had absolutely no idea what I was doing. I’m surprised I got so close to how one would properly implement an Evolutionary Algorithm.
Also, here are some more interesting statistics. I modified the mutation function a number of times, and these are the results:
-
One char, -1, 0 or +1 ascii-value: 3100 generations
-
Two chars, -1, 0 or +1 assii-value: 1924 generations
-
Three chars, -1, 0 or +1 ascii-values: 1734 generations
-
Four chars, -1, 0 or +1 ascii-values: 1706 generations
-
One char, between -4 and +4 ascii-values: 1459 generations
-
two chars: between -4 and +4 ascii-values: 2122 generations
-
Three chars, between -4 and +4 ascii-values: 4490 generations
An interesting comment on HackerNews points out:
FWIW, for this problem, at least the way the OP set it up, the "naive" algorithm is actually a very good way to go - when I increase the population size to 20, and set the mutation/selection/crossover policies OP used, I find that the average number of fitness checks required to hit "Hello, World" (about 3510) is actually higher than the number in the naive version (in the neighborhood of 3k, usually a bit under). Also, the real time taken is larger. Which means that adding "genetic" to the algorithm has actually hurt us…
In fact, even with my full GA codebase in hand (not a substantial one, I wrote it in response to this post, but it’s more flexible than the OP’s), I couldn’t find any situation where having a population size more than a few members helped - single member mutation (which is accepted/rejected if better/worse) always won. This is a good indication that this type of problem is vastly better suited to gradient descent than it is to a genetic algorithm.
6. Source code
Here are the program so you can download them and play with it a bit (ignore the SSL warning; it’s a self-signed certificate):
The Clean Algorithm is a clean implementation which allows the user to easily change the parameters (fitness, mutation probability, mutation distance, etc) of the algorithm.
7. Further reading
Here are some good reads on Evolutionary Algorithms:
This article has generated some good discussions on Reddit and Hacker News:
8. About this document
8.1. Copyright / License
Copyright (c) 2011, Ferry Boender
This document may be freely distributed, in part or as a whole, on any medium, without the prior authorization of the author, provided that this Copyright notice remains intact, and there will be no obstruction as to the further distribution of this document. You may not ask a fee for the contents of this document, though a fee to compensate for the distribution of this document is permitted.
Modifications to this document are permitted, provided that the modified document is distributed under the same license as the original document and no copyright notices are removed from this document. All contents written by an author stays copyrighted by that author.
Failure to comply to one or all of the terms of this license automatically revokes your rights granted by this license
All brand and product names mentioned in this document are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.